Creating Microsoft Windows PowerShell scripts and managing them, as well as the remote commands needed by some administrators is possible through this app
Administering systems and managing network components locally and remotely are specialized tasks better left in the hands of professionals who certainly have the appropriate tools for doing a good job.
Powershell Editor
However, several Windows components are reserved for users who are curious and ambitious to get the job done themselves, such as PowerShell. Since it's only available through the command-line shell, some users may find it difficult.
Intuitive graphical interface for PowerShell and script editor
To overcome this issue, you need a graphical interface like the one provided by Dell/Quest PowerGUI. This utility includes not only an administrative interface for PowerShell, but also a script editor that makes it possible to create and manage PowerShell files, scripts, modules and data files.
Through the PowerGUI Administrative Console, you can check out detailed information about running processes, all the system services, and event logs for applications, hardware events, Internet Explorer and other parts of the computer. There are many actions that can be carried out for each selected item (e.g. stop, suspend or resume process, modify properties, set start mode), so a complete set of administration tools are always at your disposal.

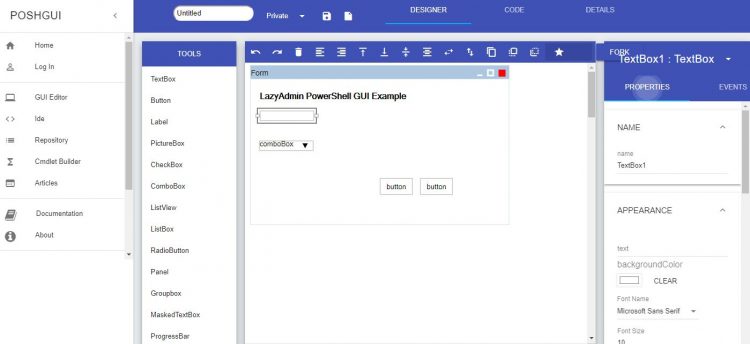
For example, our task is to build a simple GUI for a PowerShell script that shows the last password change time for the Active Directory user. In this example, we use PowerShell 3.0+ and PowerShell ISE for easy code editing. Create Windows Form with PowerShell. To use the.NET functionality to create forms, we will use the class System.Windows. About PowerShell. PowerShell is Microsoft’s task automation framework, consisting of a command-line shell and associated scripting language built on.NET. Windows PowerShell (powershell.exe) is built into Windows 7 and newer; and is optionally available for Windows 98 SP2 and newer.1 It uses.NET Framework.
View information and configure a wide range of settings
After inspecting the network configuration, you can view information for each network adapter such as IP statistics and MAC address, as well as export data to XML, HTML or CSV on the spot. With PowerGUI, you get full control over the registry keys, subkeys and their corresponding values, along with information on each drive and containing files.
Using the PowerGUI Script Editor, it's possible to load and edit existing scripts, create new ones from scratch, perform debugging jobs, compile scripts, and expand the functions of the application by loading addons.
Taking into account the rich set of features that the application offers, doubled by the ease of use that comes with all administration tasks and script authoring tasks, PowerGUI should meet the requirements of many users.
Filed under
PowerGUI was reviewed by Olivian Puha- Full support for Microsoft PowerShell 3.0
- Support for Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 as end-user platform
- Rapid access to online documentation from Administrative Console and Script Editor
- Highlight all instances of a code element in script
Powershell Editor Vi
 Read the full changelog This enables Disqus, Inc. to process some of your data. Disqus privacy policy
Read the full changelog This enables Disqus, Inc. to process some of your data. Disqus privacy policyPowerGUI 3.8.0.129
add to watchlistsend us an update- runs on:
- Windows 10 32/64 bit
Windows 2003
Windows 8 32/64 bit
Windows 7 32/64 bit
Windows Vista 32/64 bit
Windows XP
Windows 2K - file size:
- 14.4 MB
- main category:
- Programming
- developer:
top alternatives FREE
top alternatives PAID